Dogs
Bernese Mountain Dog
* Available as custom analyses. Contact us for details.
Genetic Diversity
Traits & Disorders
Genetic Ranks
Genetic Structure
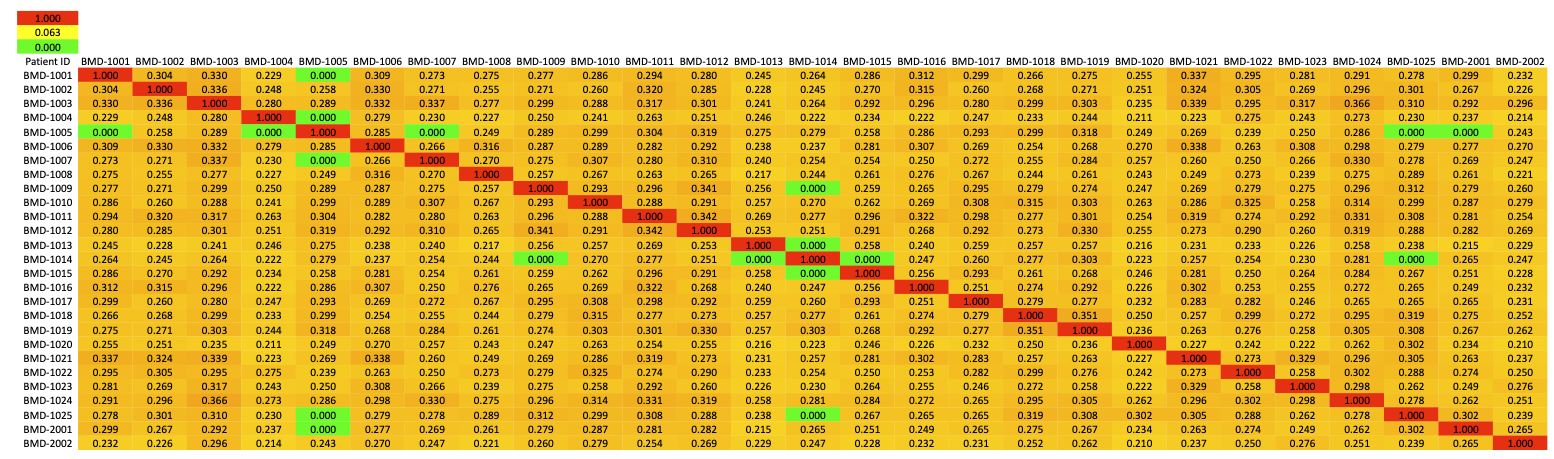
Kinship
ROH
Traits*
Health*
mtDNA & Y Haplotypes*
PCA*
Genetic Diversity
Genetic Diversity
| Dog ID | Inbreeding (F) | Inbreeding (Fis) | Mean Kinship (mk) | Heterozygosity (Ho) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| wdt_ID | Dog ID | Inbreeding (F) | Inbreeding (Fis) | Mean Kinship (mk) | Heterozygosity (Ho) |
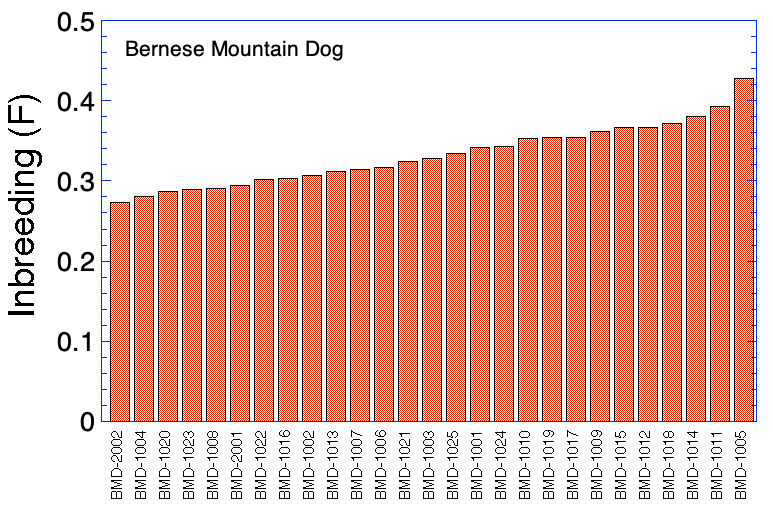
| 1 | BMD-1001 | 0.342 | 0.038 | 0.299 | 0.222 |
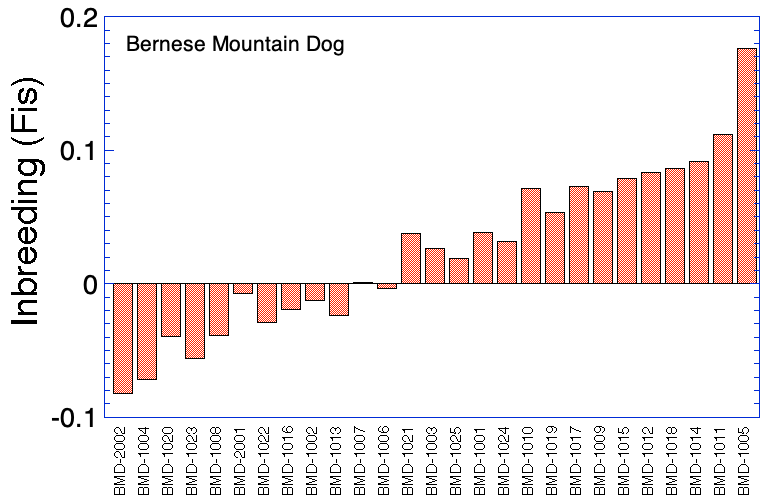
| 2 | BMD-1002 | 0.306 | -0.013 | 0.305 | 0.234 |
| 3 | BMD-1003 | 0.328 | 0.026 | 0.326 | 0.225 |
| 4 | BMD-1004 | 0.281 | -0.072 | 0.261 | 0.248 |
| 5 | BMD-1005 | 0.428 | 0.176 | 0.253 | 0.190 |
| 6 | BMD-1006 | 0.316 | -0.004 | 0.312 | 0.232 |
| 7 | BMD-1007 | 0.315 | 0.001 | 0.288 | 0.231 |
| 8 | BMD-1008 | 0.290 | -0.039 | 0.287 | 0.240 |
| 9 | BMD-1009 | 0.362 | 0.069 | 0.296 | 0.215 |
| 10 | BMD-1010 | 0.353 | 0.072 | 0.311 | 0.215 |
| 11 | BMD-1011 | 0.393 | 0.112 | 0.319 | 0.205 |
| 12 | BMD-1012 | 0.367 | 0.083 | 0.314 | 0.212 |
| 13 | BMD-1013 | 0.312 | -0.024 | 0.262 | 0.237 |
| 14 | BMD-1014 | 0.380 | 0.091 | 0.246 | 0.210 |
| 15 | BMD-1015 | 0.367 | 0.079 | 0.283 | 0.213 |
| 16 | BMD-1016 | 0.303 | -0.019 | 0.296 | 0.236 |
| 17 | BMD-1017 | 0.355 | 0.073 | 0.299 | 0.214 |
| 18 | BMD-1018 | 0.372 | 0.086 | 0.303 | 0.211 |
| 19 | BMD-1019 | 0.355 | 0.053 | 0.309 | 0.219 |
| 20 | BMD-1020 | 0.287 | -0.040 | 0.271 | 0.240 |
| 21 | BMD-1021 | 0.325 | 0.037 | 0.307 | 0.222 |
| 22 | BMD-1022 | 0.302 | -0.029 | 0.300 | 0.238 |
| 23 | BMD-1023 | 0.289 | -0.056 | 0.293 | 0.244 |
| 24 | BMD-1024 | 0.344 | 0.032 | 0.318 | 0.224 |
| 25 | BMD-1025 | 0.335 | 0.019 | 0.289 | 0.227 |
| 26 | BMD-2001 | 0.294 | -0.007 | 0.284 | 0.233 |
| 27 | BMD-2002 | 0.273 | -0.082 | 0.275 | 0.250 |
Traits & Disorders
Traits & Disorders
Genetic Ranks
Sorted by rank
Sorted by Inbreeding (F)
Sorted by Inbreeding (Fis)
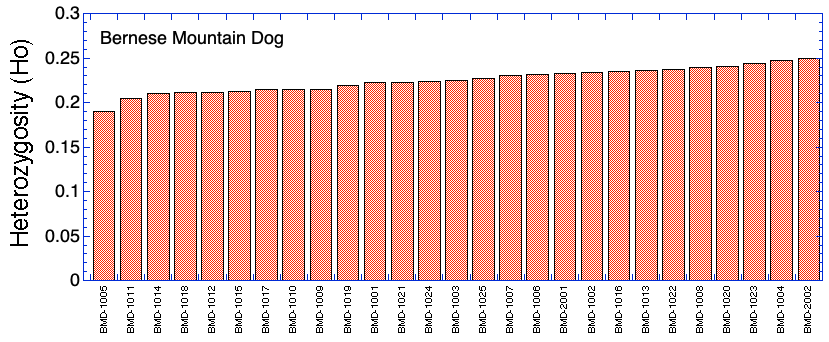
Sorted by Mean Kinship
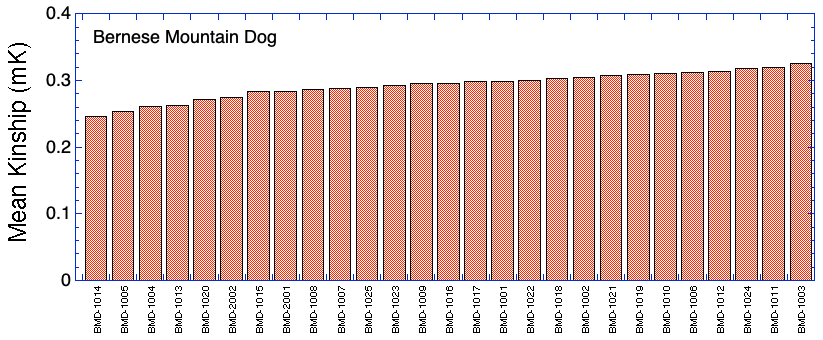
Sorted by Heterozygosity (Ho)
Genetic Structure
Genetic Structure
The dendrogram and heat map for genetic structure are produced from the kinship coefficients.
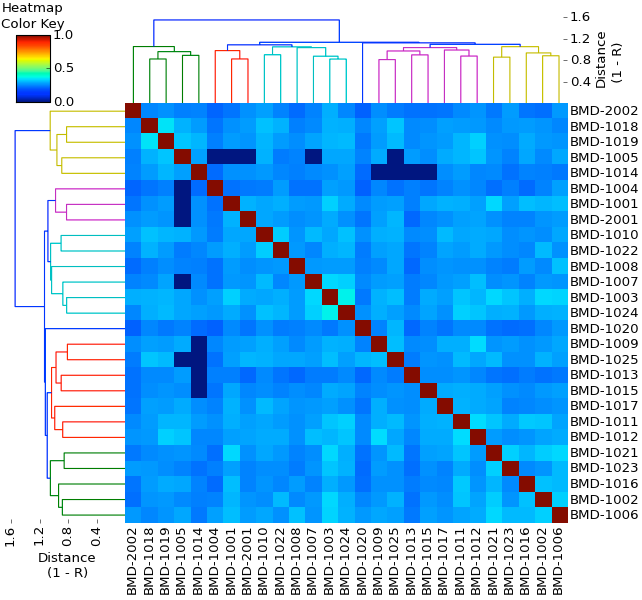
Kinship
ROH
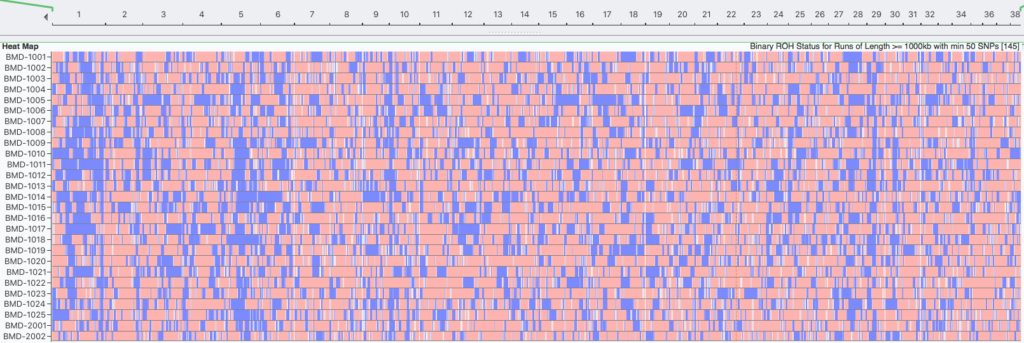
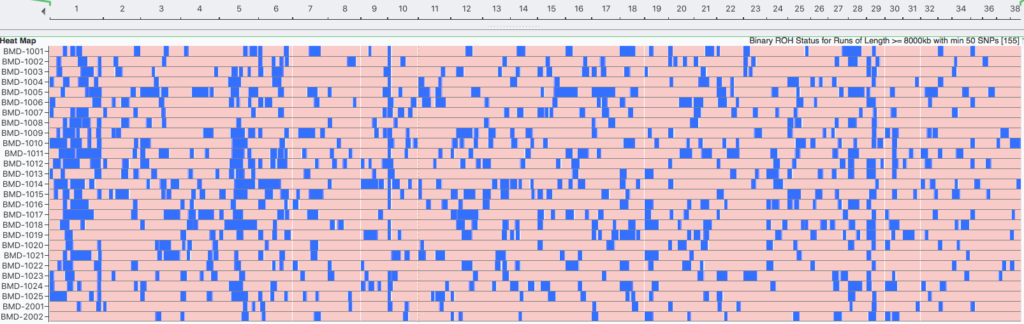
Runs of Homozygosity (ROH)
Inbreeding tends to produce runs (blocks) of homozygosity (ROH) on the chromosomes. Over time, the crossing-over of chromosomes during meiosis can split up blocks of homozygosity, so the largest blocks are likely to be the most recent inbreeding and smaller blocks reflect older inbreeding. ROH are used to estimate inbreeding from SNP data.
Learn more about Runs of Homozygosity.
Inbreeding: 25 generations (1000 kb)
Inbreeding: 6 generations (8000 kb)
Traits*
Health*
mtDNA & Y Haplotypes*
PCA*