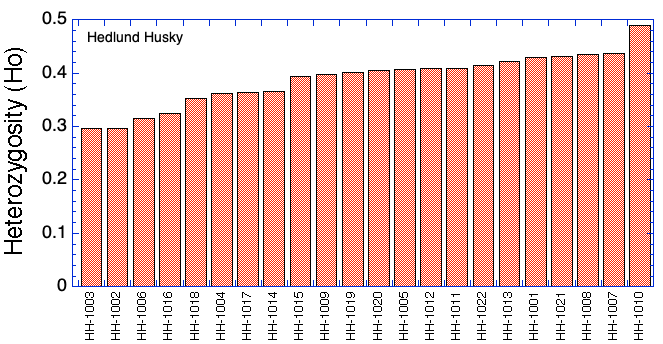
Hedlund Husky: Members
Sorted by rank
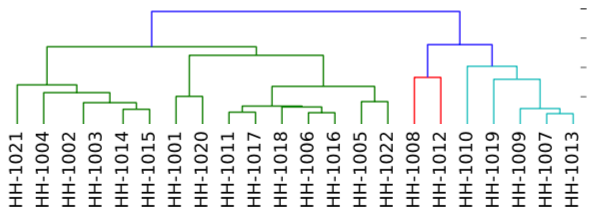
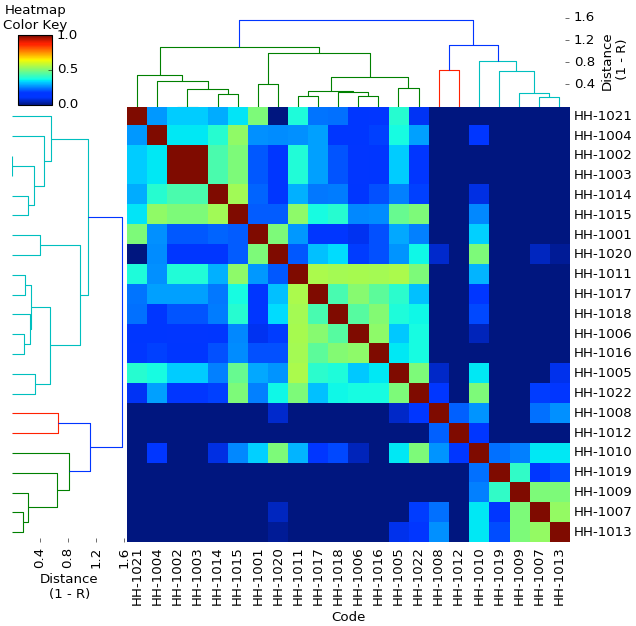
The dendrogram and heat map for genetic structure are produced from the kinship coefficients.
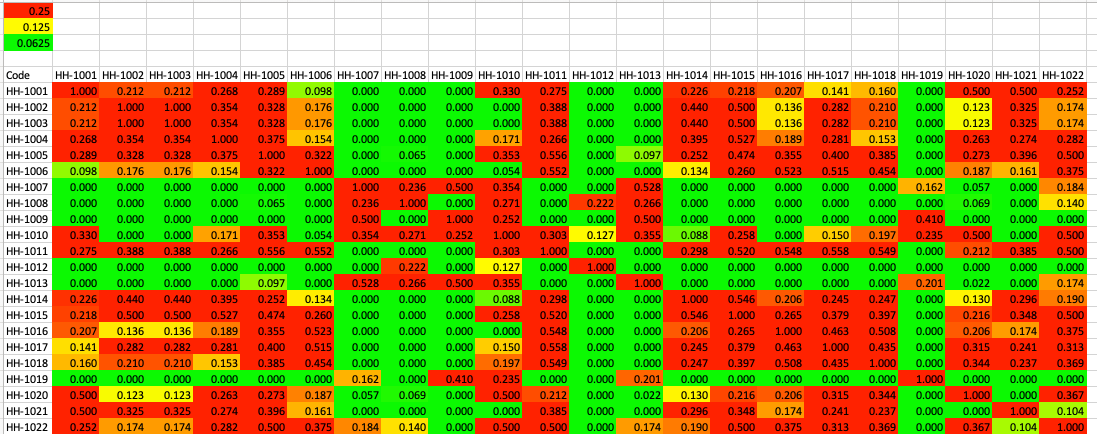
Kinship Coefficients & Litter COI
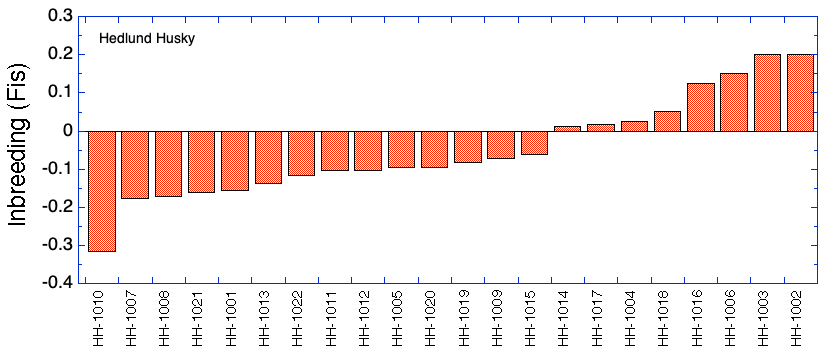
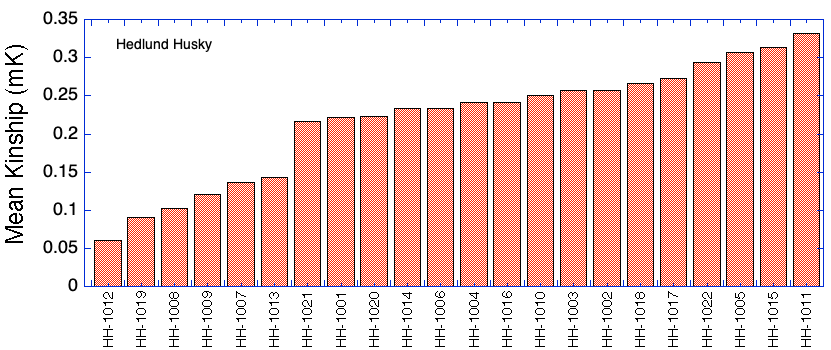
The kinship coefficient (K) is the fraction of the genome shared by two individuals that is homozygous by descent, so it is a pairwise measure of relatedness.
This kinship matrix is color coded to identify cells in which K < 0.0625 (6.25%; green, equivalent to a cross of first cousins), K = 0.125 (12.5%; yellow, half-sib cross), and K > 0.25 (25%; red, full sib cross). The kinship coefficient between a male and female is also the predicted average inbreeding coefficient of their offspring if they produced a litter.
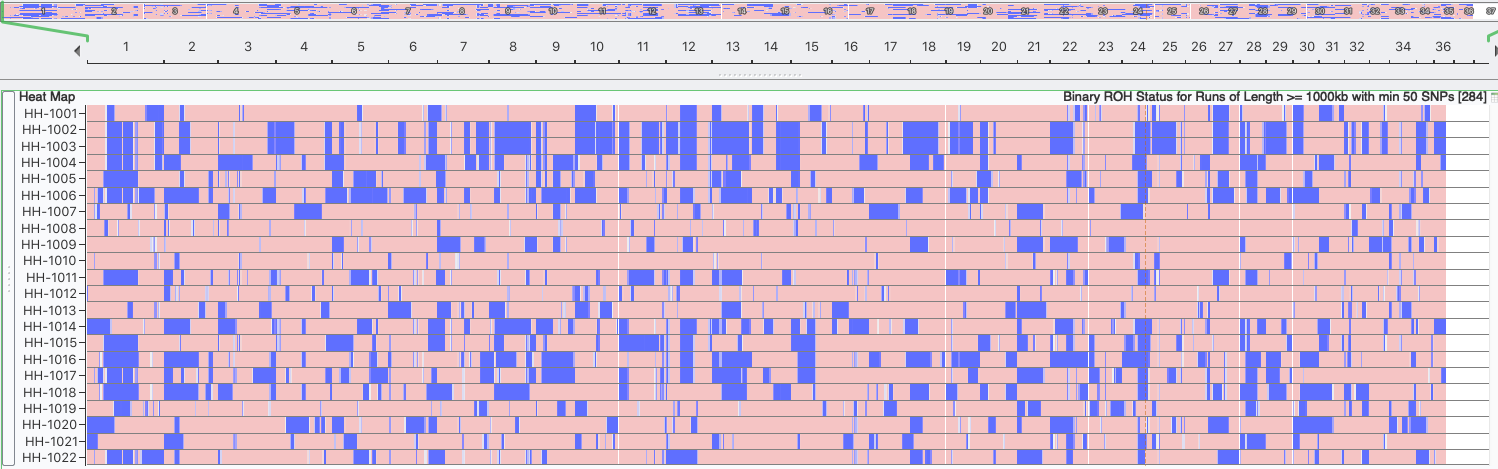
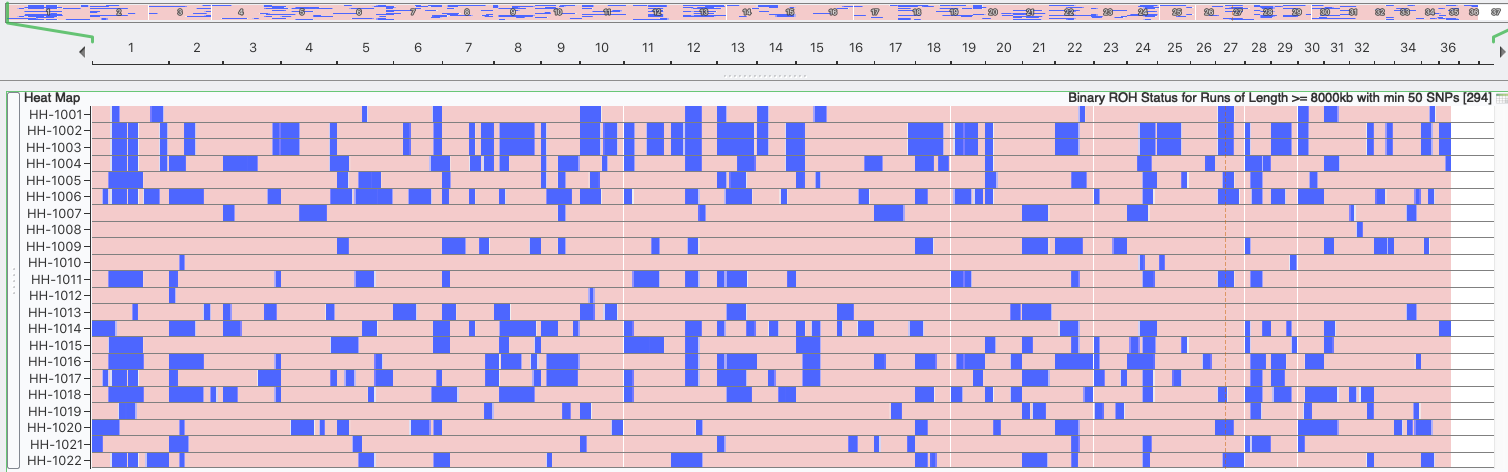
Runs of Homozygosity
Inbreeding tends to produce runs (blocks) of homozygosity (ROH) on the chromosomes. Over time, the crossing-over of chromosomes during meiosis can split up blocks of homozygosity, so the largest blocks are likely to be the most recent inbreeding and smaller blocks reflect older inbreeding. ROH are used to estimate inbreeding from SNP data.
Learn more about Runs of Homozygosity.
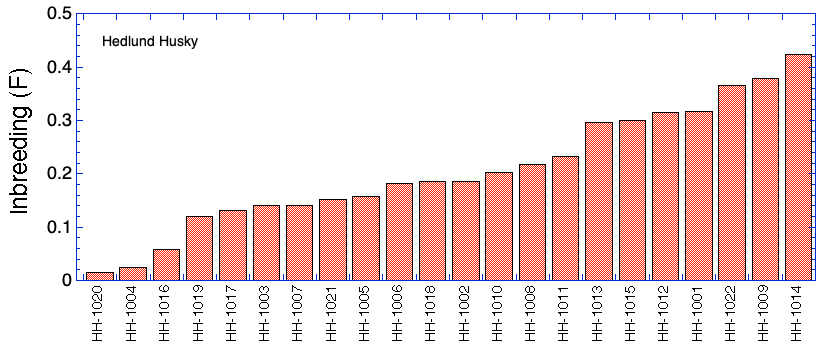
Inbreeding: 25 generations (1000 kb)
Inbreeding: 6 generations (8000 kb)
CODES
mtDNA haplotypes
x – A29a
ww- A11a
xxx- A247
ooo- A16/17/99/100
Y chromosome haplotypes
x- Hc.1
xxx- Ha.4
Coat Color
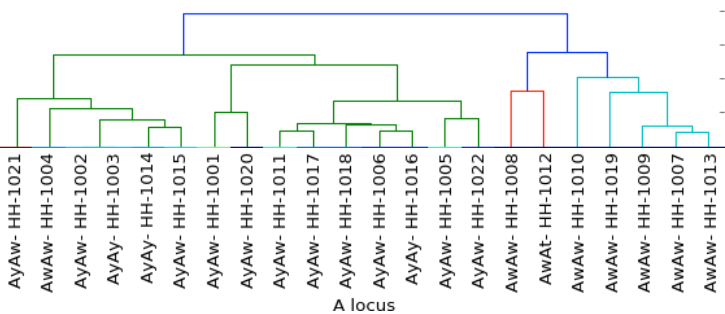
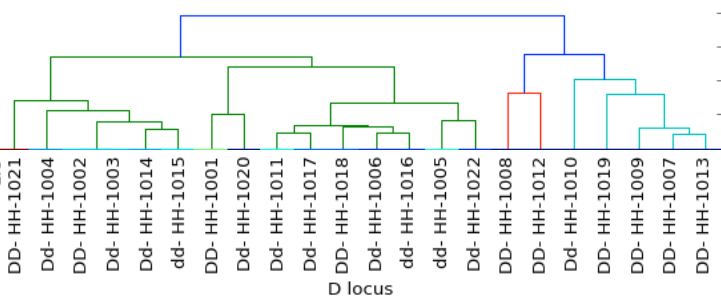
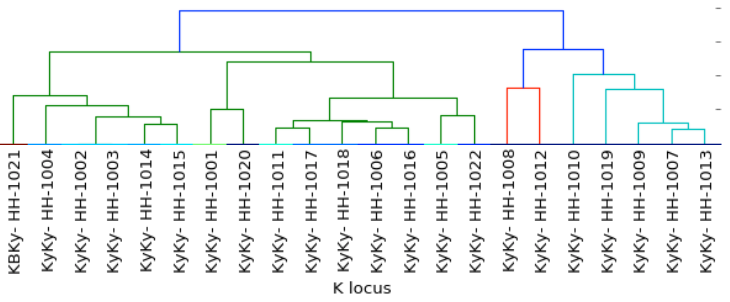
c- clear
xx- carrier
xxxx- homozygous
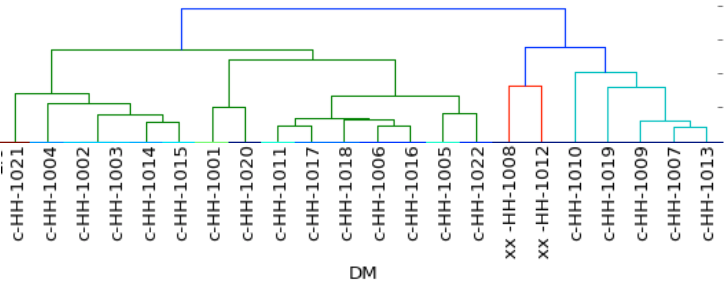
Degenerative Myelopathy
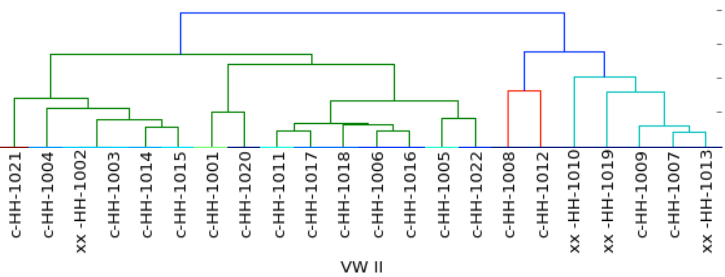
Von Willebrands Disease II (VWF Exon 28)
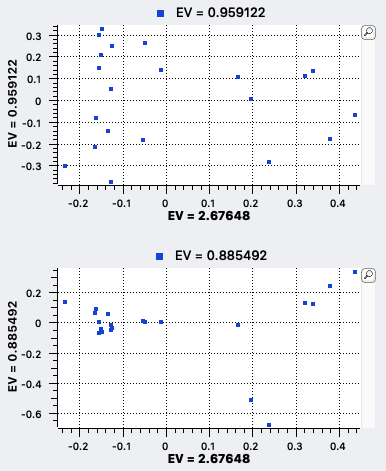
Principal Components Analysis